The Commonwealth of Australia is a union of six states and various territories. The Australian mainland is made up of five states and three territories, with the sixth state of Tasmania being made up of islands. In addition there are six island territories, known as external territories, and a claim to a territory in Antarctica. All states and two of the three internal territories have their own parliaments and administer themselves; the remaining territories are administered by the Federal Government.
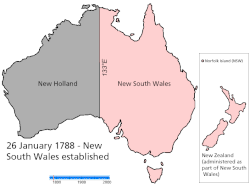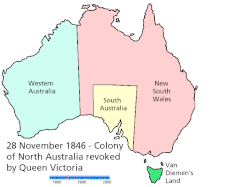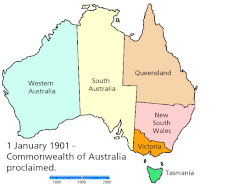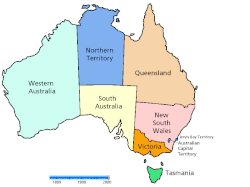
Map showing the creation of the colonies/states and mainland territories.
States and territories[]
| Flag | State/Territory name | ISO[2] | Postal | Type | Capital (or largest settlement) | Population | Area (km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashmore and Cartier Islands | External | (West Islet) | 0 | 199 | |||
| Australian Antarctic Territory | External | (Mawson Station) | 1,000 | 5,896,500 | |||
| Australian Capital Territory | AU-ACT | ACT | Territory | Canberra | 358,894 | 2,358 | |
| Christmas Island | CX | External | Flying Fish Cove | 1,493 | 135 | ||
| Cocos (Keeling) Islands | CC | External | West Island | 628 | 14 | ||
| Coral Sea Islands | External | (Willis Island) | 4 | 10 | |||
| Heard Island and McDonald Islands | HM | External | (Atlas Cove) | 0 | 372 | ||
| Jervis Bay Territory | JBT | Territory | (Jervis Bay Village) | 611 | 70 | ||
| New South Wales | AU-NSW | NSW | State | Sydney | 7,238,819 | 800,642 | |
| Norfolk Island | NF | External | Kingston | 2,114 | 35 | ||
| Northern Territory | AU-NT | NT | Territory | Darwin | 229,675 | 1,349,129 | |
| Queensland | AU-QLD | QLD | State | Brisbane | 4,516,361 | 1,730,648 | |
| South Australia | AU-SA | SA | State | Adelaide | 1,644,642 | 983,482 | |
| Tasmania | AU-TAS | TAS | State | Hobart | 507,626 | 68,401 | |
| Victoria | AU-VIC | VIC | State | Melbourne | 5,547,527 | 227,416 | |
| Western Australia | AU-WA | WA | State | Perth | 2,296,411 | 2,529,875 |
See also: List of State Codes
Australia has had three now-defunct territories in its history:
- From 1926 to 1931, the Northern Territory was divided into Central Australia and North Australia, with the border at the 20th parallel of latitude. Both territories were reincorporated as the Northern Territory at the end of this period.
- From 1949 to 1975, the Territory of Papua and New Guinea was part of Australia, remaining so until the independence of the country of Papua New Guinea.
Background and overview[]
The states originated as separate British colonies prior to Federation (in 1901). Their powers are protected by the Australian constitution, and Commonwealth legislation only applies to the states where permitted by the constitution. The territories, by contrast, are from a constitutional perspective directly subject to the Commonwealth government. The Australian Parliament has powers to legislate in the territories that it does not possess in the states.
Most of the territories are directly administered by the Commonwealth government, while three (the Northern Territory, the Australian Capital Territory and Norfolk Island) administer themselves. In the self-governing territories the Australian Parliament retains the full power to legislate, and can override laws made by the territorial institutions, which it has done on rare occasions. For the purposes of Australian (and joint Australia-New Zealand) intergovernmental bodies, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory are treated as states.
Furthermore, the distribution of powers between the Commonwealth and the territories is different from that between the Commonwealth and the states. In the Northern Territory, the Commonwealth retains the power to directly administer uranium mining and Aboriginal lands – powers which it does not possess with respect to the states.
Each state has a Governor, appointed by the Queen, which by convention she does on the advice of the state Premier. The Administrators of the Northern Territory and Norfolk Island are, by contrast, appointed by the Governor-General. The Australian Capital Territory has neither a Governor nor an Administrator, but the Governor-General exercises some powers that in other jurisdictions are exercised by the Governor of a state or Administrator of a territory, such as the power to dissolve the Legislative Assembly.
Jervis Bay Territory is unique in being the only non-self-governing territory that is not an external territory. Until 1989 it was a part of the ACT, but was separated when the ACT achieved self-government. Residents of the Jervis Bay Territory are not represented in the ACT Legislative Assembly. However, laws made by that assembly generally apply to them. They are represented in the Australian parliament as part of the Electoral Division of Fraser in the ACT and by the ACT's two Senators. In other respects, the territory is administered directly by the Federal Government through the Territories portfolio.
Each state has a bicameral Parliament except Queensland, which abolished its upper house in 1922. The lower house is called the Legislative Assembly, except in South Australia and Tasmania, where it is called the House of Assembly. Tasmania is the only state to use proportional representation for elections to its lower house; all others elect members from single member constituencies, using instant-runoff voting(preferential voting). The upper house is called the Legislative Council, and is generally elected from multi-member constituencies using proportional representation. The three self-governing territories, the ACT, the Northern Territory and Norfolk Island, have unicameral Legislative Assemblies.
The head of government of each state is called the Premier, appointed by the state's Governor. In normal circumstances the Governor will appoint as Premier whoever leads the party or coalition which exercises control of the lower house (in the case of Queensland, the only house) of the state Parliament. However, in times of constitutional crisis, the Governor can appoint someone else as Premier. The head of government of the self-governing internal territories is called the Chief Minister. The Northern Territory's Chief Minister, in normal circumstances whoever controls the Legislative Assembly, is appointed by the Administrator.
Comparative terminology[]
| Entity | State/Territory type | Tie to the Queen? | Domestic administrator | Head of Government | Upper House of Parliament | Lower House of Parliament | Member of Parliament* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Federal Government | Direct | Governor-General | Prime Minister | Senate | House of Representatives | Senator | MP |
| South Australia | Federated state | Direct (established by Australia Act) | Governor | Premier | Legislative Council | House of Assembly | MLC | MHA |
| Tasmania | ||||||||
| New South Wales | Legislative Assembly | MLA | ||||||
| Victoria | ||||||||
| Western Australia | ||||||||
| Queensland | None (abolished 1922) | None | MP | |||||
| Australian Capital Territory | Self-governing territory | None | Assembly and Chief Minister | Chief Minister | None | Legislative Assembly | None | MLA |
| Northern Territory | Indirect (through Governor-General) | Administrator | Administrator | |||||
| Norfolk Island | External territory | |||||||
| Christmas Island | Mayor/Shire President | Shire Council | Councillor | |||||
| Cocos (Keeling) Islands | ||||||||
| *Note: The abbreviation MP is an acceptable, and indeed more common, term for members of each lower house. | ||||||||
Statistics[]
| State/territory | Land area (km²) | Rank | Population (2006) | Rank | Population density (/km²) | Rank | % of population in capital | Rank |
| 2,358 | 8th | 344,200 | 7th | 137.53 | 1st | 99.6% | 1st | |
| 800,642 | 5th | 6,967,200 | 1st | 8.44 | 3rd | 63% | 5th | |
| 227,416 | 6th | 5,297,600 | 2nd | 22 | 2nd | 71% | 4th | |
| 1,730,648 | 2nd | 4,279,400 | 3rd | 2.26 | 5th | 46% | 7th | |
| 983,482 | 4th | 1,601,800 | 5th | 1.56 | 6th | 73.5% | 2nd | |
| 2,529,875 | 1st | 2,163,200 | 4th | 0.79 | 7th | 73.4% | 3rd | |
| 68,401 | 7th | 498,200 | 6th | 7.08 | 4th | 41% | 8th | |
| 1,349,129 | 3rd | 219,900 | 8th | 0.15 | 8th | 54% | 6th |
Distance table[]
| Adelaide | |||||||||||||||
| 2673 | Albany | ||||||||||||||
| 1533 | 3588 | Alice Springs | |||||||||||||
| 1578 | 3633 | 443 | Uluru | ||||||||||||
| 2045 | 4349 | 3038 | 3254 | Brisbane | |||||||||||
| 2483 | 1943 | 2483 | 1223 | 3317 | Broome | ||||||||||
| 3352 | 5656 | 2457 | 2900 | 1716 | 2496 | Cairns | |||||||||
| 1196 | 3846 | 3706 | 2751 | 1261 | 3275 | 2568 | Canberra | ||||||||
| 3022 | 4614 | 1489 | 1932 | 3463 | 1803 | 2882 | 4195 | Darwin | |||||||
| 1001 | 3674 | 2534 | 2579 | 1944 | 3636 | 3251 | 918 | 4023 | Hobart | ||||||
| 3219 | 3787 | 1686 | 2129 | 3660 | 1045 | 3079 | 4392 | 827 | 4220 | Kununurra | |||||
| 2783 | 5087 | 2505 | 2948 | 976 | 2840 | 740 | 1999 | 2930 | 2682 | 3127 | Mackay | ||||
| 731 | 3404 | 2264 | 2309 | 1674 | 3124 | 2981 | 648 | 3753 | 609 | 3950 | 2412 | Melbourne | |||
| 2742 | 5106 | 1209 | 1652 | 1829 | 1834 | 1248 | 2561 | 1634 | 3075 | 1831 | 1296 | 2805 | Mount Isa | ||
| 2781 | 409 | 3696 | 3741 | 4457 | 2389 | 5764 | 3954 | 4205 | 3782 | 3378 | 5195 | 3512 | 4905 | Perth | |
| 1412 | 3970 | 3830 | 2875 | 1001 | 3373 | 2495 | 286 | 4034 | 1142 | 4516 | 1926 | 872 | 2400 | 4078 | Sydney |
Distance in kilometres from the corresponding city on the X-Y axis.
State and territory codes[]
| State/Territory | Call signs | Postal | Telephone area codes | Time zone | ||||
| AM/FM | TV | Amateur | Abbrev. | Postcode | Std | Summer | ||
| Australian Capital Territory | 1xx(x)† | xx(x)Cn† | VK1xx† | ACT | 02nn*, 26nn, 29nn | 02 | +10 | +11 |
| New South Wales | 2xx(x) | xx(x)Nn | VK2xx | NSW | 1nnn*, 2nnn | 02 | +10(+10½) | +11 |
| Victoria | 3xx(x) | xx(x)Vn | VK3xx | VIC | 3nnn, 8nnn* | 03 | +10 | +11 |
| Queensland | 4xx(x) | xx(x)Qn | VK4xx | QLD | 4nnn, 9nnn* | 07 | +10 | |
| South Australia | 5xx(x) | xx(x)Sn | VK5xx | SA | 5nnn | 08 | +9½ | +10½ |
| Western Australia | 6xx(x) | xx(x)Wn | VK6xx | WA | 6nnn | 08 | +8 | |
| Tasmania | 7xx(x) | xx(x)Tn | VK7xx | TAS | 7nnn | 03 | +10 | +11 |
| Northern Territory | 8xx(x) | xx(x)Dn | VK8xx | NT | 08nn | 08 | +9½ | |
| External Territories | ||||||||
| Norfolk Island | 2xx(x) | VK9xx | (NSW) | +672 3 | +11½ | |||
| Christmas Island | (WA) | (WA) | +7 | |||||
| Cocos Island | +6½ | |||||||
| Australian Antarctic Territory | none | VK0xx | (Tas) | +672 1 | +6 to +8 | |||
| Macquarie Island | none | +10 | +11 | |||||
| * used for some PO box and Large Users only. † a number of broadcast stations in the ACT have call signs allocated as if it was part of New South Wales. | ||||||||
See also[]
- ISO 3166-2:AU, the ISO codes for the states and territories of Australia.
- List of regions in Australia
References and notes[]
External links[]
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||

