| Founded | 1902 |
|---|---|
| Founder(s) | Thomas B. Jeffery |
| Defunct | 1916 |
| Headquarters | Kenosha, Wisconsin, United States |
| Industry | trucks, armoured cars |
The Thomas B. Jeffery Company was an American automobile manufacturer in Kenosha, Wisconsin from 1902 until 1916. The company manufactured the Rambler and Jeffery brand motorcars. It was preceded by the Gormully & Jeffery Manufacturing Company (a bicycle company) and it was the parent company to Nash Motors, thus one of the parent companies of American Motors and Chrysler.
Thomas B. Jeffery[]

Thomas B. Jeffery

Thomas B. Jeffery and his 1897 Rambler prototype
Thomas B. Jeffery was an inventor and an industrialist. He was one of America's first entrepreneurs interested in automobiles in the late 19th century. In 1897, he built his first prototype motorcar. Thomas B. Jeffery was serious enough about automobiles to sell his stake in Gormully & Jeffery to the American Bicycle Company to finance the new car company.
Business[]

Charles T. Jeffery driving a 1901 Rambler model A

Charles T. Jeffery (left) Charles W. Nash (right)
Charles T. Jeffery's (Thomas' son) experimental prototypes of 1901 (Models A & B) used at least two radical innovations - steering wheels and front-mounted engines. By the time Charles was ready for production in 1902, his father had talked him out of these wild dreams and convinced him to stick with tillers and engines under the seat.
From 1902 until 1908, Jeffery moved steadily to bigger, more reliable models. Jeffery cars were built on assembly lines (the second manufacturer to adopt them -- Ransom E. Olds was first), and in 1903 Jeffery sold 1,350 Ramblers. By 1905, Jeffery more than doubled this number. One reason may have been because Charles went back to the steering wheel before 1904. In 1907, Jeffery was building a large variety of different body styles and sizes. Among them was a five-passenger, US$2,500 Rambler weighing 2,600 pounds (1179 kg) and powered by a 40-horsepower (30 kW) engine.
In April, 1910, Thomas B. Jeffery, died in Pompeii, Italy and in June of that year the business was incorporated under the name of the Thomas B. Jeffery Company, with Charles T. Jeffery as the president and general manager, H. W. Jeffery, vice president and treasurer.
In 1915, Charles T. Jeffery, changed the automotive branding from Rambler to Jeffery to honor the founder, his father, Thomas B. Jeffery.
As of 1916, G. H. Eddy replaced H.W. Jeffery as the treasurer so H.W. Jeffery could focus on the position of vice president. G. W. Greiner was the secretary, L. H. Bill the general manager, J. W. DeCou the factory manager, and Al Recke was the sales manager.
Charles T. Jeffery survived the sinking of the RMS Lusitania (a British luxury liner torpedoed by the Germans in World War I) in 1915 and decided to spend the rest of his life in a more enjoyable manner. Charles W. Nash resigned from General Motors, saw an opportunity and bought the Thomas B. Jeffery Company in August 1916.

1916 Jeffery Truck sold at auction in 2006
The Factory[]
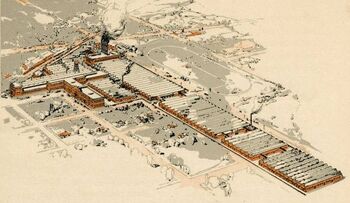
The sprawling Jeffery works circa 1915

Jeffery factory building

Jeffery company employees
Jeffery, with the money from his sale of Gormully & Jeffery, bought the old Sterling Bicycle Company's factory in Kenosha, Wisconsin. The original factory building was only 600 x 100 feet (183 x 30 m) in size. However, by 1916, the company's buildings expanded over 20 acres (8 ha) under roof and the facilities had grown to over 100 acres (40 ha) including a test track.
Quad[]
During World War I, Jeffery designed a four wheel drive truck, known as the "Quad" or Jeffery Quad and Nash Quad that assisted the Allied effort. These unique vehicles saw heavy service under General John J. "Blackjack" Pershing.

1915 Jeffery Armoured car
Approximately 11,500 Jeffery and Nash Quads were built. "Four-wheel drive trucks had been built before ... but aside from the Jeffery Quad (Nash Quad, per subsequent purchase) earlier designs were inefficient, crude, and flimsy."[1] The Quad not only had four-wheel drive and four-wheel brakes, but also four-wheel steering.[2]
Timeline[]
- 1897 - Jeffery builds a rear-engine Rambler prototype using the Rambler name previously used on a highly successful line of bicycles made by Gormully & Jeffery.
- 1899 - Positive reviews at the 1899 Chicago International Exhibition & Tournament and the first National Automobile Show in New York City prompt the Jefferys to enter the automobile business.
- 1900 (Dec 6) - Thomas B. Jeffery finalizes a US$65,000 deal to buy the Kenosha, factory of the defunct Sterling Bicycle with money from the sale of his interest in Gormully & Jeffery.[3]
- 1901 - Two more prototypes, Models A and B, are made.
- 1902 - First production Ramblers - the US$750 Model C open runabout and the $850 Model D (the same car with a folding top). Both are powered by an 8-horsepower (6 kW), 98 in³ (1.6 L) one-cylinder engine mounted beneath the seat, and are steered by a right-side tiller. First-year production totals 1,500 units making Jeffery the second-largest car maker behind Oldsmobile.
- 1910 (Mar 21) - Thomas B. Jeffery dies while on vacation in Italy.
- 1910 (Jun 10) - Charles incorporates the firm as a US$3 million public stock company.
- 1914 - The Rambler name is replaced with the Jeffery moniker in honor of the founder.
- 1916 (Aug) - Charles Jeffery sells the company to former General Motors Corp. President Charles W. Nash.
- 1917 - Charles Nash renames the Jeffery Motor Company, Nash Motors after himself.
References[]
| This page uses some content from Wikipedia. The original article was at Thomas B. Jeffery Company. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with Tractor & Construction Plant Wiki, the text of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons by Attribution License and/or GNU Free Documentation License. Please check page history for when the original article was copied to Wikia |
- ↑ Mroz, Albert (2009). American Military Vehicles of World War I: An Illustrated History of Armored Cars, Staff Cars, Motorcycles, Ambulances, Trucks, Tractors and Tanks. McFarland & Company, 19. ISBN 9780786439607.
- ↑ Eckermann, Erik (2001). World history of the automobile. Society of Automotive Engineers, 76. ISBN 9780768008005. Retrieved on 3 September 2010.
- ↑ "Rear View Mirror: 103 Years Ago" Ward's Auto World, December 1, 2003. Retrieved on: July 16, 2007.
