| Transmission types |
|---|
|
|
|

Part-cutaway view of the Volkswagen Group 6-speed Direct-Shift Gearbox. The concentric multi-plate clutches have been sectioned, along with the mechatronics module. This also shows the additional power take-off for distributing torque to the rear axle for four-wheel drive applications. - View this image with annotations
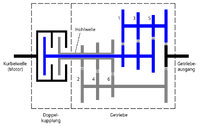
Schematic diagram of a dual clutch transmission
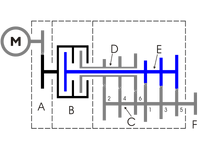
Dual-clutch gearbox:
M: Motor
A: Primary drive
B: Double Clutch
C: shaft
D: main shaft, even gears
E: main shaft, odd gears
F: Output
A direct-shift gearbox (German: Direkt-Schalt-Getriebe[1]), commonly abbreviated to DSG,[2][3] is an electronically controlled dual-clutch[2] multiple-shaft manual gearbox, in a transaxle design – without a conventional clutch pedal,[4] and with full automatic,[2] or semi-manual control. The first actual dual-clutch transmissions derived from Porsche in-house development for 962 racing cars in the 1980s.
In simple terms, a DSG is two separate manual gearboxes (and clutches), contained within one housing, and working as one unit.[2][3][5] It was designed by BorgWarner,[4] and was initially licensed to the Volkswagen Group, with support by IAV GmbH.[citation needed] By using two independent clutches,[2][5] a DSG can achieve faster shift times,[2][5] and eliminates the torque converter of a conventional epicyclic automatic transmission.[2]
Overview[]
Transverse DSG[]
At the time of launch in 2003[2][6] - it became the world's first dual clutch transmission in a series production car,[2][6] in the German-market Volkswagen Golf Mk4 R32[2][6] and shortly afterwards, worldwide in the original Audi TT 3.2;[7] and for the first few years of production, this original DSG transmission was only available in transversely orientated[2] front-engine, front-wheel-drive — or Haldex Traction-based four-wheel-drive vehicle layouts.
The first DSG transaxle that went into production for the Volkswagen Group mainstream marques had six forward speeds (and one reverse),[6][7] and used wet/submerged multi-plate clutch packs[2][4] (Volkswagen Group internal code: DQ250, parts code prefix: 02E).[7][8] It has been paired to engines with up to 350 N·m (260 lb·ft) of torque,[6][7] and the two-wheel-drive version weighs 93 kg (210 lb). It is manufactured at Volkswagen Group's Kassel plant,[2] with a daily production output of 1,500 units.[6]
At the start of 2008, another world first,[6] an additional 70 kg (150 lb) seven-speed DSG transaxle[6] (Volkswagen Group internal code: DQ200, parts code prefix: 0AM)[8][9][10] became available. It differs from the six-speed DSG, in that uses two single-plate dry clutches (of similar diameter).[10] This clutch pack was designed by LuK Clutch Systems, LLC.[11] This seven-speed DSG is used in smaller front-wheel-drive cars with smaller displacement engines with lower torque outputs,[6][7][10] such as the latest Volkswagen Golf,[6][10] Volkswagen Polo Mk5,[10] and the new SEAT Ibiza,[7] due to it having a maximum torque handling capacity of 250 N·m (180 lb·ft).[6] It has considerably less oil capacity than the six-speed DQ250; this new DQ200 uses just 1.7 litres (0.37 imp gal/0.45 US gal) of transmission fluid.[6]
In September 2010, VW launched a new seven-speed DSG built to support 500 N·m (370 lb·ft), the DQ500. Its first use was in the Audi TT-RS.[citation needed]
Audi longitudinal DSG[]
In late 2008, an all-new seven-speed longitudinal[7][12] S tronic[12] version of the DSG transaxle went into series production (Volkswagen Group internal code: DL501, parts code prefix: 0B5),[8] led by Audi transmission design engineer Mario Schenker.[12] Initially, from early 2009, it is only used in certain Audi cars, and only with longitudinally mounted engines. Like the original six-speed DSG, it features a concentric dual wet multi-plate clutch.[12] However, this particular variant uses notably more plates — the larger outer clutch (for the odd-numbered gears) uses 10 plates, whereas the smaller inner clutch (driving even-numbered gears and reverse) uses 12 plates.[12] Another notable change over the original transverse DSGs is the lubrication system[13][14] — Audi now utilise two totally separate oil circuits.[12] One oil circuit, consisting of 7.5 litres (1.65 imp gal/1.98 US gal), lubricates the hydraulic clutches and mechatronics with fully synthetic specialist automatic transmission fluid (ATF),[12] whilst the other oil circuit lubricates the gear trains and front and centre differentials with 4.3 litres (0.95 imp gal/1.14 US gal) of conventional hypoid gear oil.[12] This dual circuit lubrication is aimed at increasing overall reliability, due to eliminating cross-contamination of debris and wear particles.[12] It has a torque handling limit of up to 600 N·m (440 lb·ft),[7] and engine power outputs of up to 330 kW (450 PS/440 bhp).[7] It has a total mass, including all lubricants and the dual-mass flywheel of 141.5 kg (312 lb).[7]
This was initially available in their quattro all-wheel-drive variants,[8] and is very similar to the new ZF Friedrichshafen-supplied[15] Porsche Doppel-Kupplung (PDK).[16][17]
Operational introduction[]
The internal combustion engine drives two clutch packs.[2][4][5] The outer clutch pack drives gears 1, 3, 5[2][4] (and 7 when fitted), and reverse[2] — the outer clutch pack has a larger diameter compared to the inner clutch, and can therefore handle greater torque loadings. The inner clutch pack drives gears 2, 4, and 6.[2][4] Instead of a standard large dry single-plate clutch, each clutch pack for the six-speed DSG is a collection of four small wet interleaved clutch plates (similar to a motorcycle wet multi-plate clutch). Due to space constraints, the two clutch assemblies are concentric, and the shafts within the gearbox are hollow and also concentric.[5] Because the alternate clutch pack's gear-sets can be pre-selected[2][4][5] (predictive shifts enabled via the 'unused' section of the gearbox), un-powered time while shifting is avoided[2][5] because the transmission of torque is simply switched from one clutch-pack to the other.[2] This means that the DSG takes only about 8 milliseconds to upshift.[3][4] In comparison, the sequential manual transmission (SMT) in the Ferrari F430 Scuderia takes 60 milliseconds to shift,[18] or 150 milliseconds in the Ferrari Enzo.[3] The quoted time for upshifts is the time the wheels are completely non-powered.
DSG controls[]
The direct-shift gearbox utilises a floor-mounted transmission shift lever, very similar to that of a conventional automatic transmission.[10] The lever is operated in a straight 'fore and aft' plane (without any 'dog-leg' offset movements), and utilises an additional button to help prevent an inadvertent selection of an inappropriate shift lever position.
"P"[]
P position of the floor-mounted gear shift lever means that the transmission is set in "Park". Both clutch packs are fully disengaged, all gear-sets are disengaged, and a solid mechanical transmission 'lock' is applied to the crown wheel of the DSG's internal differential. This position must only be used when the motor vehicle is stationary. Furthermore, this is the position which must be set on the shift lever before the vehicle ignition key can be removed.
"N"[]
N position of the floor-mounted shift lever means that the transmission is in "neutral". Similar to P above, both clutch packs and all gear-sets are fully disengaged, however the parking lock is disengaged. This position should be used when the motor vehicle is stationary for a period of time, such as at red traffic lights, or waiting in a queue of stationary traffic.[19] The DSG should not be held in any of the active gear modes while stationary using the footbrake for other than brief periods — due to the clutches being held on the bite point, as this can overheat the clutches and transmission fluid. This position also allows the engine to be restarted (in some cars needing the key to be partially disengaged) which cannot be done in any of the active modes.[19]
"D" mode[]
Whilst the motor vehicle is stationary and in neutral (N), the driver can select D for "drive" (after first pressing the foot brake pedal). The transmission's reverse gear is selected on the first shaft k1,[3] and the outer clutch K2 engages at the start of the 'bite point'. At the same time, on the alternate gear shaft, the reverse gear clutch K1 is also selected[2][3] (pre-selected), gearbox still doesn't know whether the customer wants to go forward or reverse (could still change even though its in d) but the clutch pack for second gear (k2) get ready to engage . When the driver releases the foot brake pedal, the k2 clutch pack increases the clamping force, allowing the second gear to take up the drive through an increase of the 'bite point', and therefore transferring the torque from the engine through the transmission to the driveshafts and roadwheels — and the vehicle moves forward. Pressing the throttle / accelerator pedal will fully engage the clutch, and causes an increase of forward vehicle speed, pressing the throttle pedal to the floor (hard acceleration) will cause the gear box to kick down to first gear to provide the acceleration associate with first although there will be a slight hesitation while the mechatronics deselects second gear and selects first gear as the vehicle accelerates, the transmission's computer determines when the second gear (which is connected to the second clutch) should be fully utilised. Depending on the vehicle speed, and amount of engine power being requested by the driver (full throttle, or part-throttle normal driving),[4] the DSG then upshifts. During this sequence, the DSG disengages the first outer clutch whilst simultaneously engaging the second inner clutch[2][3][4] (all power from the engine is now going through the second shaft), thus completing the shift sequence. This sequence happens in 8 milliseconds (aided by pre-selection),[3][4] and can happen even with full throttle opening, and as a result, there is virtually no power loss.[2][4]
Once the vehicle has completed the shift to second gear, the first gear is immediately de-selected, and third gear (being on the same shaft as 1st and 5th) is pre-selected,[2][3][4] and is pending. Once the time comes to shift into 3rd, the second clutch disengages and the first clutch re-engages.[2] This method of operation continues in the same manner up to 6th (or top) gear.
Downshifting is similar to upshifting but in reverse order, and is slower, at 600 milliseconds, due to the engine's Electronic Control Unit, or ECU, needing to 'blip' the throttle, so that the engine crankshaft speed can match the appropriate gear shaft speed.[2][4] The car's computer senses the car slowing down, or more power required (during acceleration), and thus engages a lower gear on the shaft not in use, and then completes the downshift.
The actual shift points are determined by the DSG's transmission ECU, which commands a hydro-mechanical unit.[2] The transmission ECU, combined with the hydro-mechanical unit, are collectively called a "mechatronics"[2] unit or module. Because the DSG's ECU uses "fuzzy logic", the operation of the DSG is said to be "adaptive"; that is, the DSG will "learn" how the user drives the car, and will progressively tailor the shift points accordingly to suit the habits of the driver.
In the vehicle instrument display, between the speedometer and tachometer, the available shift-lever positions are shown, the current position of the shift-lever is highlighted (emboldend), and the current gear ratio in use is also displayed as a number.
Under "normal", progressive and linear acceleration and deceleration, the DSG shifts in a "sequential" manner, i.e. under acceleration: 1st > 2nd > 3rd > 4th > 5th > 6th; and the same sequence reversed for deceleration. However, the DSG can also skip the normal sequential method, by 'missing out' adjacent gears, and shift two or more gears.[3] This is most apparent if the car is being driven at sedate speeds in one of the higher gears with a light throttle opening, and the accelerator pedal is then pressed down, engaging the "kick-down" function. During kick-down, the DSG will skip gears,[10] shifting directly to the most appropriate gear depending on speed and throttle opening. (This kick-down may be engaged by any increased accelerator pedal opening, and is completely independent of the additional resistance to be found when the pedal is pressed fully to the floor, which will activate a similar kick-down function when in Manual operation mode. On the seven-speed unit in the 2007 on Audi variants, will not automatically shift to 6th gear... maxing out at 5th to keep power available at high RPM while cruising.
When the floor-mounted gear selector lever is in position D, the DSG works in fully automatic mode,[3][5] with emphasis placed on gear shifts programmed to deliver maximum fuel economy.[3][10] That means that shifts will change up and down very early in the rev-range. As an example, on the Volkswagen Golf Mk5 GTI, sixth gear will be engaged around 52 km/h (32 mph), when initially using the DSG transmission with the 'default' ECU adaptation - although with an "aggressive" or "sporty" driving style, the adaptive shift pattern will increase the vehicle speed at which sixth gear engages.
"S" mode[]
The floor selector lever also has an S position.[2] When S is selected, "sport" mode[2] is activated in the DSG. Sport mode still functions as a fully automatic mode,[3] identical in operation to "D" mode, but upshifts and downshifts are made much higher up the engine rev-range.[2][3][10] This aids a more sporty driving manner,[2] by utilising considerably more of the available engine power, and also maximising engine braking. However, this mode does have a detrimental effect on the vehicle fuel consumption, when compared to D mode. This mode may not be ideal to use when wanting to drive in a 'sedate' manner; nor when road conditions are very slippery, due to ice, snow or torrential rain — because loss of tyre traction may be experienced (wheel spin during acceleration, and may also result in roadwheel locking during downshifts at high engine rpms under closed throttle). On 4motion or quattro-equipped vehicles this may be partially offset by the drivetrain maintaining full-time engagement of the rear differential in 'S' mode, so power distribution under loss of front-wheel traction may be marginally improved.
S is highlighted in the instrument display, and like D mode, the currently used gear ratio is also displayed as a number.
"R"[]
R position of the floor-mounted shift lever means that the transmission is in "reverse". This functions in a similar way to D, but there is just one 'reverse gear'. When selected, R is highlighted in the instrument display.
Manual mode[]
Additionally, the floor shift lever also has another plane of operation, for manual[3][5] mode, with spring-loaded "+" and "−" positions. This plane is selected by moving the stick away from the driver (in vehicles with the driver's seat on the right, the lever is pushed to the left, and in left-hand drive cars, the stick is pushed to the right) when in "D" mode only. When this plane is selected, the DSG can now be controlled like a manual gearbox, albeit only under a sequential shift pattern.
In most (VW) applications, the readout in the instrument display changes to 6 5 4 3 2 1, and just like the automatic modes, the currently used gear ratio is highlighted or emboldened. In other versions (e.g. on the Audi TT) the display shows just M followed by the gear currently selected, e.g. M1, M2 etc.
To change up a gear, the lever is pushed forward (against a spring pressure) towards the "+", and to change down, the lever is pulled rearward towards the "−". The DSG transmission can now be operated with the gear changes being (primarily) determined by the driver. This method of operation is commonly called "tiptronic".[2] In the interests of engine preservation, when accelerating in Manual/tiptronic mode, the DSG will still automatically change up just before the redline, and when decelerating, it will change down automatically at very low revs, just before the engine idle speed (tickover). Furthermore, if the driver calls for a gear when it is not appropriate (e.g.: requesting a downshift when engine speed is near the redline) the DSG will not change to the driver's requested gear.[3]
Current variants of the DSG will still downshift to the lowest possible gear ratio when the kick-down button is activated during full throttle whilst in manual mode. In Manual mode this kick-down is only activated by an additional button at the bottom of the accelerator pedal travel; unless this is pressed the DSG will not downshift, and will simply perform a full-throttle acceleration in whatever gear was previously being utilised.
Paddle shifters[]
Initially available on certain high-powered cars, and those with a "sporty" trim level — such as those using the 2.0 TFSI and 3.2/3.6 VR6 engines[2] — steering wheel-mounted paddle shifters[3][5] were available. However, these are now being offered (either as a standard inclusive fitment, or as a factory optional extra) on virtually all DSG-equipped cars, throughout all model ranges, including lesser power output applications, such as the 105 PS Volkswagen Golf Plus.[10]
These operate in an identical manner as the floor mounted shift lever when it is placed across the gate in manual mode. The paddle shifters have two distinct advantages: the driver can safely keep both hands on the steering wheel when using the Manual/tiptronic mode; and the driver can immediately manually override either of the automatic programmes (D or S) on a temporary basis,[10] and gain instant manual control of the DSG transmission[10] (within the above described constraints).
If the paddle-shift activated manual override of one of the automatic modes (D or S) is utilised intermittently, the DSG transmission will "default" back to the previously selected automatic mode after a predetermined duration of inactivity of the paddles, or when the vehicle becomes stationary. Alternatively, should the driver wish to immediately revert to fully automatic control, this can be done by activating and holding the "+" paddle[10] for at least two seconds.
Advantages and disadvantages[]
- Advantages
- Better fuel economy[2][6] (up to 15% improvement) than conventional planetary geared automatic transmission (due to lower parasitic losses from oil churning)[5] and for some models with manual transmissions;[2]
- No loss of torque transmission from the engine to the driving wheels during gear shifts;[2][4][5]
- Short up-shift time of 8 milliseconds when shifting to a gear the alternate gear shaft has preselected;[3][4]
- Smooth gear-shift operations;[4][5]
- Consistent shift time of 600 milliseconds, regardless of throttle or operational mode;[4]
- Disadvantages
- Achieving maximum acceleration or hill climbing, while avoiding engine speeds higher than a certain limit (e.g. 3000 or 4000 RPM), is difficult since it requires avoiding triggering the kick-down-switch. Avoiding triggering the kick-down-switch requires a good feel of the throttle pedal, but use of full throttle can still be achieved with a little sensitivity as the kick-down button is only activated beyond the normal full opening of the accelerator pedal.
- Marginally worse overall mechanical efficiency compared to a conventional manual transmission, especially on wet-clutch variants (due to electronics and hydraulic systems);[5]
- Expensive specialist transmission fluids/lubricants with dedicated additives are required, which need regular changes;[13][14]
- Relatively expensive to manufacture,[citation needed] and therefore increases new vehicle purchase price;
- Relatively lengthy shift time when shifting to a gear ratio which the transmission ECU did not anticipate (around 1100 ms, depending on the situation);[4][20]
- Torque handling capability constraints perceive a limit on after-market engine tuning modifications (though many tuners and users have now greatly exceeded the official torque limits.[citation needed]); Later variants have been fitted to more powerful cars, such as the 300 bhp/350Nm VW R36 and the 272 bp/350 Nm Audi TTS.
- Heavier than a comparable Getrag conventional manual transmission (75 kg (170 lb) vs. 47.5 kg (105 lb));
- Mechatronic units in earlier models are prone to problems and requires replacement units
Applications[]
- For applications of similar transmissions in other vehicles beyond Volkswagen Groups DSG and S tronic, see dual clutch transmission.
Volkswagen Group vehicles with the DSG gearbox include:[8]
Audi[]
After originally using the 'DSG' moniker, Audi subsequently renamed their direct-shift gearbox to "S tronic".
- Audi TT
- Audi A1
- Audi A3
- Audi S3
- Audi A4 (B8)[7][12]
- Audi S4 (B8)[7][12]
- Audi A5
- Audi A7
- Audi A8 (D4)
- Audi Q5[7][12]
Bugatti[]
SEAT[]
- SEAT Ibiza
- SEAT León
- SEAT Altea
- SEAT Toledo
- SEAT Alhambra
Škoda[]
- Škoda Fabia
- Škoda Octavia
- Škoda Roomster
- Škoda Superb II
- Škoda Yeti
Volkswagen Passenger Cars[]
- Volkswagen Polo
- Volkswagen Golf, GTI, TDI, R32[2][6]
- Volkswagen Jetta & Bora
- Volkswagen Eos
- Volkswagen Touran[6]
- Volkswagen New Beetle
- Volkswagen New Beetle Convertible
- Volkswagen Passat and R36
- Volkswagen Passat CC
- Volkswagen Sharan
- Volkswagen Scirocco
- Volkswagen Tiguan 2011
Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles[]
- Volkswagen Caddy car-derrived van
- Volkswagen Transporter (T5) medium van[22]
Problems and Recall of DSG-equipped vehicles[]
United States of America[]
In August 2009, Volkswagen of America issued two recalls of DSG-equipped vehicles. The first involved 13,500 vehicles,[23] and was to address unplanned shifts to the neutral gear,[23] while the second involved similar problems (by then attributed to faulty temperature sensors) and applied to 53,300 vehicles.[23][24][25] These recalls arose as a result of investigations carried out by the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA),[26] where owners reported to the NHTSA a loss of power whilst driving.[23] This investigation preliminary found only 2008 and 2009 model year vehicles as being affected.[23][26]
Other markets, such as Volkswagen group Australia, are yet to admit this being a widespread issue and refuse to offer similar recall programs as their US counterparts, even though multiple reports of similar incidents and failures have occurred.
China[]
Since 2009 there have been widespread concerns from Chinese consumers particularly among the online community, expressed that Volkswagen has failed to respond to complaints about defects in its DSG-equipped vehicles. Typical issues associated with 6-speed DSG include abnormal noise and unable to change gear; while issues associated with 7-speed DSG include abnormal noise, excessive shift shock, abnormal increase in engine RPM, flashing gear indicator on the dashboard as well as unable to shift to even-numbered gears.[27] In March 2012 China’s quality watchdog the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ) has said it has been in contact with Volkswagen (China) and urged the carmaker to probe the issues.[28][29] In a survey held by Gasgoo.com (China) of the 2,937 industry experts and insiders, 83% respondent believe that the carmaker should consider a full vehicle recall.[30] In March 2012 Volkswagen Group China has admitted there could be an issue in its seven-speed DSG gearboxes that may affect approximately 500,000 vehicles from its various subsidiaries in China.[31] A software upgrade has since been offered to the affected vehicles in an attempt to repair the problem.
According to 163.com - one the China's most popular web portals, in March 2012 about a quarter of the complaints about problems found in cars in China's automotive market were against DSG-equipped vehicles manufactured by Volkswagen.[32] The top five models that dominate those complaints were:
- Volkswagen Magotan - 6%
- Volkswagen Bora - 5.3%
- Volkswagen Sagitar - 5.3%
- Volkswagen Touareg - 4.7%
- Volkswagen Golf - 4%
See also[]
- Volkswagen 01M transmission
- list of ZF transmissions
- list of Aisin transmissions
- list of GM transmissions
- list of Ford transmissions
- Continuously variable transmission (CVT)
- Multimode manual transmission
References[]
- ↑
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33 2.34 2.35 2.36 2.37 Volkswagen Group / Volkswagen AG (22 November 2002). "Volkswagen DSG - World's first dual-clutch gearbox in a production car", https://www.volkswagen-media-services.com/medias_publish/ms/content/en/pressemitteilungen/2002/11/22/volkswagen_dsg_-_world.standard.gid-oeffentlichkeit.html. Retrieved on .
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 3.17 "Twin Clutch / Direct Shift Gearbox (DSG) - What it is, how it works". Cars.About.com. Retrieved on 27 October 2009.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17 4.18 Mark Wan. "Gearbox Transmission - Twin-Clutch Gearbox". AutoZine.org. AutoZine Technical School. Retrieved on 27 October 2009.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 "How the Dual Clutch Transmission Works". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (2009). Retrieved on 27 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 "The 7-speed DSG - the intelligent automatic gearbox from Volkswagen". VolkswagenAG.com. Volkswagen Group / Volkswagen AG (21 January 2008). Retrieved on 3 November 2009.
- ↑ 7.00 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 7.10 7.11 7.12 "Volkswagen Group extends reach of dual clutch transmissions". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (8 May 2009). Retrieved on 27 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 ETKA[clarification needed]
- ↑
- ↑ 10.00 10.01 10.02 10.03 10.04 10.05 10.06 10.07 10.08 10.09 10.10 10.11 10.12 "Golf Plus on the Road". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (2009). Retrieved on 28 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ "LuK Dual Dry Clutch 7-Speed DSG Gearbox in volume production at Volkswagen". LuKclutch.com. Schaeffler Group USA Inc., BÜHL, GERMANY (13 February 2008). Retrieved on 27 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ 12.00 12.01 12.02 12.03 12.04 12.05 12.06 12.07 12.08 12.09 12.10 12.11 "Inside Audi’s premium DCT". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (8 May 2009). Retrieved on 27 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Special Transmissions Need Special Lubricants". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (2009). Retrieved on 28 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Special Transmissions Need Special Lubricants". DCTFacts.com. Retrieved on 15 May 2011.
- ↑ "ZF 7-speed dual clutch transmission". ZF.com. ZF Friedrichshafen AG. Retrieved on 28 October 2009.
- ↑ "Top 911 moves to industry-standard shift controls". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (24 September 2009). Retrieved on 27 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ "Porsche Joins the DCT Set". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation. Retrieved on 28 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ Mark Wan (17 October 2007). "Ferrari F430 Scuderia". AutoZine.org. Retrieved on 27 October 2009.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "Mitsubishi Evo X - Precautions". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (9 March 2009). Retrieved on 28 October 2009. “engage neutral while waiting at lights or in a traffic queue, rather than holding the car on the footbrake – a practice which could lead to overheating”[dead link]
- ↑ "How Dual-Clutch Transmissions Work". AutoEvolution.com. SoftNews NET (31 March 2009). Retrieved on 30 October 2009.
- ↑ "Ricardo Extends DCT Production for Open-top Bugatti". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (16 January 2009). Retrieved on 28 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ "Volkswagen (Commercial Vehicles) medium van is first with DCT". DCTfacts.com. The Lubrizol Corporation (24 September 2009). Retrieved on 27 October 2009.[dead link]
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 23.4 Jensen, Christopher (21 August 2009). "VW DSG Transmission Problem Leads to Recall", wheels.blogs.nytimes.com, The New York Times Company. Retrieved on 30 November 2009.
- ↑ Chang, Richard S. (28 August 2009). "VW Has More Problems With Its DSG Transmission", wheels.blogs.nytimes.com, The New York Times Company. Retrieved on 30 November 2009.
- ↑ "Volkswagen will repair DSG transmissions on 53,300 vehicles". Blog.CarAndDriver.com. Hachette Filipacchi Media U.S., Inc., (28 August 2009). Retrieved on 27 October 2009.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 ODI Resume - Volkswagen of America, Inc., 2008-2009 Volkswagen EOS, GTI, Jetta and R32 with DSG transmissionPDF, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Retrieved 30 November 2009. The direct shift gearbox can malfunction at any speed and cause the vehicle to lose motive power suddenly and without warning
- ↑ Template error: argument title is required.
- ↑ Template error: argument title is required.
- ↑ Template error: argument title is required.
- ↑ "Analysis: Industry viewpoints on VW's Chinese DSG gearbox controversy", Gasgoo. Retrieved on 2012-04-05.
- ↑ "VW issues software upgrade to resolve gearbox problems, shies away from recall", Gasgoo. Retrieved on 2012-04-05.
- ↑ Template error: argument title is required.
External links[]
Official links[]
Independent links[]
- Pictures and diagrams of DQ250 DSG at WorldCarFans.com
- Reviews, videos, and explanation of DSG transmission
- First Drive: Audi TT 3.2 DSG review at VWvortex.com
- European interest in dual clutch technology shifts up a gear - informative article from Just-Auto.com
- Computer-controlled Meccano model of a DSG Transmission by Alan Wenbourne of the South East London Meccano Club (SELMEC)
- Video of Alan Wenbourne's Meccano DSG in operation at YouTube.com
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Bugatti road car timeline, 1910–present — a marque of the Volkswagen Group since 1998 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| type / class |
1910s | 1920s | 1930s | 1940s | 1950s | 1960s | 1963–86 | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | ||
| owner | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| company name |
S.p.A |
S.A.S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| touring car |
Type 30 / Type 49 | Type 57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type 46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| limousine | Type 41 Royale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| roadster | Type 13 / Brescia Tourer | Type 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| coupé | Type 101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| sports car |
Type 13 | Type 18 Garros | Type 252 | EB110 | Veyron EB16.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| founder: Ettore Bugatti • Bugatti corporate website • A marque of the Volkswagen Group • Molsheim | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This page uses some content from Wikipedia. The original article was at Direct-Shift Gearbox. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with Tractor & Construction Plant Wiki, the text of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons by Attribution License and/or GNU Free Documentation License. Please check page history for when the original article was copied to Wikia |